This reference is for Processing 2.0+. If you have a previous version, use the reference included with your software. If you see any errors or have suggestions, please let us know. If you prefer a more technical reference, visit the Processing Javadoc.
| Name | blue() |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Examples | 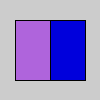 color c = color(175, 100, 220); // Define color 'c' fill(c); // Use color variable 'c' as fill color rect(15, 20, 35, 60); // Draw left rectangle float blueValue = blue(c); // Get blue in 'c' println(blueValue); // Prints "220.0" fill(0, 0, blueValue); // Use 'blueValue' in new fill rect(50, 20, 35, 60); // Draw right rectangle | ||
| Description |
Extracts the blue value from a color, scaled to match current colorMode(). The value is always returned as a float, so be careful not to assign it to an int value. The blue() function is easy to use and understand, but it is slower than a technique called bit masking. When working in colorMode(RGB, 255), you can acheive the same results as blue() but with greater speed by using a bit mask to remove the other color components. For example, the following two lines of code are equivalent means of getting the blue value of the color value c: float b1 = blue(c); // Simpler, but slower to calculate float b2 = c & 0xFF; // Very fast to calculate |
||
| Syntax | blue(rgb) | ||
| Parameters |
| ||
| Returns | float | ||
| Related | red() green() alpha() hue() saturation() brightness() >> (right shift) |
