This reference is for Processing 2.0+. If you have a previous version, use the reference included with your software. If you see any errors or have suggestions, please let us know. If you prefer a more technical reference, visit the Processing Javadoc.
| Name |
mag() |
| Examples | 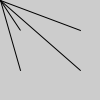
float x1 = 20;
float x2 = 80;
float y1 = 30;
float y2 = 70;
line(0, 0, x1, y1);
println(mag(x1, y1)); // Prints "36.05551"
line(0, 0, x2, y1);
println(mag(x2, y1)); // Prints "85.44004"
line(0, 0, x1, y2);
println(mag(x1, y2)); // Prints "72.8011"
line(0, 0, x2, y2);
println(mag(x2, y2)); // Prints "106.30146"
|
|---|
| Description |
Calculates the magnitude (or length) of a vector. A vector is a direction in space commonly used in computer graphics and linear algebra. Because it has no "start" position, the magnitude of a vector can be thought of as the distance from the coordinate 0,0 to its x,y value. Therefore, mag() is a shortcut for writing dist(0, 0, x, y).
|
| Syntax | mag(a, b)
mag(a, b, c) |
|---|
| Parameters |
| a |
float: first value |
| b |
float: second value |
| c |
float: third value |
|
| Returns | float |
|---|
| Related | dist()
|
|---|
Updated on May 19, 2014 05:30:00pm PDT

