This reference is for Processing 2.0+. If you have a previous version, use the reference included with your software. If you see any errors or have suggestions, please let us know. If you prefer a more technical reference, visit the Processing Javadoc.
| Name | randomGaussian() |
|---|---|
| Examples | 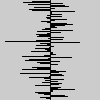
for (int y = 0; y < 100; y++) {
float x = randomGaussian() * 15;
line(50, y, 50 + x, y);
}

float[] distribution = new float[360];
void setup() {
size(100, 100);
for (int i = 0; i < distribution.length; i++) {
distribution[i] = int(randomGaussian() * 15);
}
}
void draw() {
background(204);
translate(width/2, width/2);
for (int i = 0; i < distribution.length; i++) {
rotate(TWO_PI/distribution.length);
stroke(0);
float dist = abs(distribution[i]);
line(0, 0, dist, 0);
}
}
|
| Description | Returns a float from a random series of numbers having a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1. Each time the randomGaussian() function is called, it returns a number fitting a Gaussian, or normal, distribution. There is theoretically no minimum or maximum value that randomGaussian() might return. Rather, there is just a very low probability that values far from the mean will be returned; and a higher probability that numbers near the mean will be returned. |
| Syntax | randomGaussian() |
| Returns | float |
| Related | random() noise() |
